Land for housing and sustainable urbanisation

In the Arab region, 60 per cent of people live in urban centres and over a quarter of urban dwellers – about 82 million people - live in slums.
Land for housing
Good land governance and functioning land administration are essential enablers for the provision of adequate housing for all. Land defines three key dimensions of adequate housing: tenure security, affordability, and location. Access to land is the first step towards obtaining a home. Land use planning, land markets, land prices, availability of well-located and serviced land affect the availability of affordable housing. The exclusion from adequate housing reinforces socio-economic and spatial inequalities and impede access to urban services. In many cities, the ability to buy and own housing or land has become the dominant factor in perpetuating inequality. The Arab Land Initiative aims to improve the understanding of the relation between land and adequate housing in the region, to inform change in policies and practices.
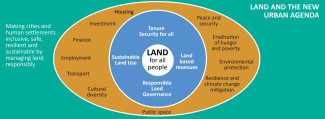
Land and sustainable urbanisation
Land is a key driver of inclusive and sustainable urban development. It underpins key aspects of the implementation of the New Urban Agenda and of SDG 11.
Good urban land governance and tenure security of urban and periurban dwellers are crucial for green, resilient, and connected cities that enable inclusive economic growth and safe and affordable housing. Efficient and effective land use and planning, better management of natural resources, and more equitable regional development are crucial for both urban and rural areas.
Tenure security is associated with national economic growth, increase in per capita income, rising private investments and productivity. It secures investments, facilitates access to credit and supports service delivery, allowing for more inclusive growth, in both rural and urban economies.
Functioning land administration and management systems are a fundamental infrastructure for the proper functioning of urban land markets: they are essential to shape urban growth though land use planning and to improve the efficiency in the use and allocation of limited land. Land administration is pivotal for the effective provision of urban services and infrastructure to enable connectivity and maximize the competitiveness of urban centres.
Taxes on land and real property have the potential to constitute one of the most stable sources of revenues for local governments. Good practices in property taxation and valuation enhance fiscal independence and the capacity of local governments to finance urban development.
The Arab Land Initiative aims to improve the understanding of the relation between land and sustainable urbanisation in the region, to inform change in policies and practices.


